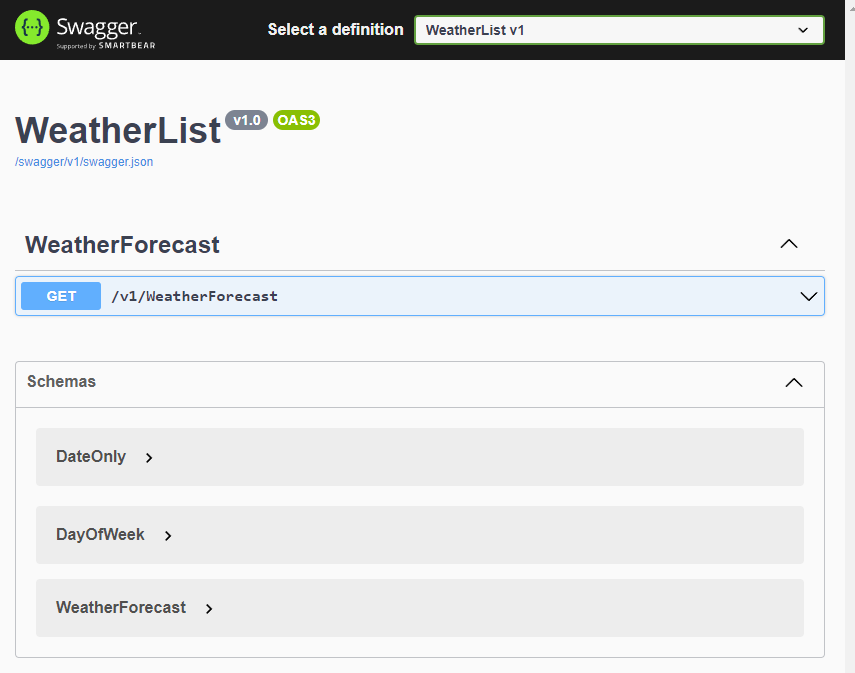
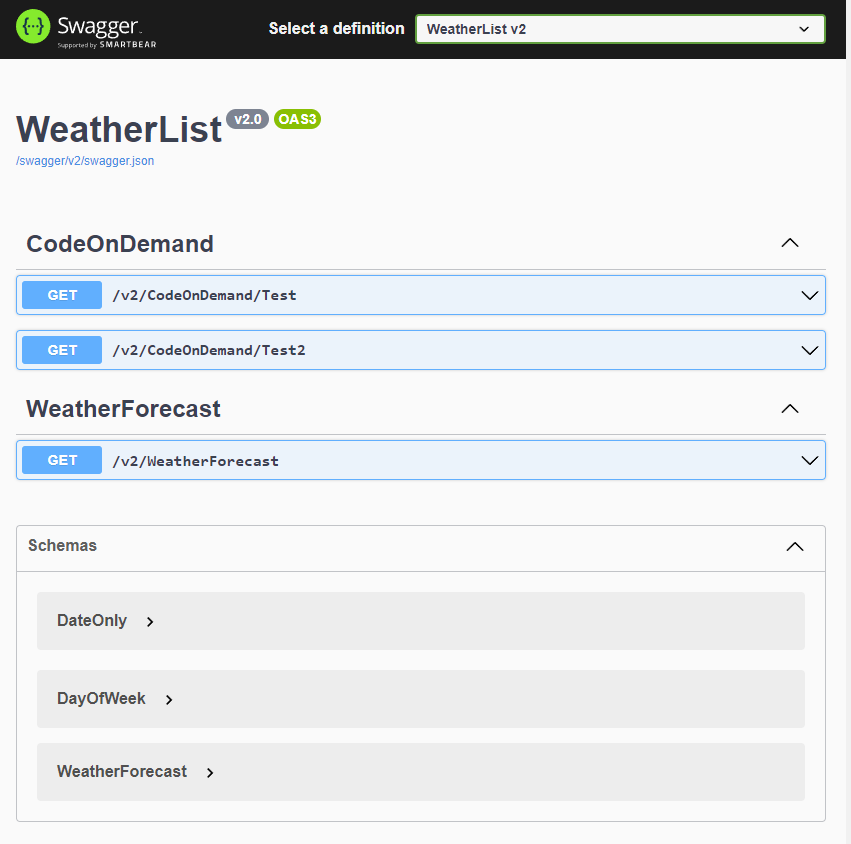
Api Versioning in ASP.Net Core
Here are the most common API versioning techniques:
URI versioning: by using a a different domain or URL segment for each version. E.g: site.com/v1/Method
Query string versioning: by using a GET parameter in the URL. E.g: site.com/Method?api-version=1.0
Route versioning: by using a different route. E.g: site.com/Method-v1, site.com/Method-v2
Media Type versioning: using the standard Accept HTTP header to indicate the version like: Accept: application/json;api-version=2.0
Header versioning: using a custom HTTP Header like Accept-Version:2.0
The most used versioning format used is semantic versioning, also known as SemVer which is basically: MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
MAJOR version when you make incompatible API changes
MINOR version when you add functionality in a backward compatible manner
PATCH version when you make backward compatible bug fixes
URI versioning with ASP.Net Core
Install the required packages:
- Asp.Versioning.Mvc
- Asp.Versioning.Mvc.ApiExplorer
Basic Services Configuration:
builder.Services.AddApiVersioning(options => {
options.ReportApiVersions = true;
options.ApiVersionReader = new UrlSegmentApiVersionReader();
options.AssumeDefaultVersionWhenUnspecified = true;
options.DefaultApiVersion = new ApiVersion(1, 0);
}) // From Package: Asp.Versioning.Mvc
.AddApiExplorer(options => {
// version format as "'v'major[.minor][-status]"
options.GroupNameFormat = "'v'VVV";
// this option is used when versioning by url segment
options.SubstituteApiVersionInUrl = true;
}); // From Package: Asp.Versioning.Mvc.ApiExplorerSwagger Configuration (Optional)
builder.Services.AddSwaggerGen(options => {
options.SwaggerDoc(
"v1",
new OpenApiInfo { Title = "WeatherList", Version = "v1.0" });
options.SwaggerDoc(
"v2",
new OpenApiInfo { Title = "WeatherList", Version = "v2.0" });
});
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseSwagger();
app.UseSwaggerUI(options => {
options.SwaggerEndpoint(
$"/swagger/v1/swagger.json",
$"WeatherList v1");
options.SwaggerEndpoint(
$"/swagger/v2/swagger.json",
$"WeatherList v2");
});
}Folder-based versioning structure
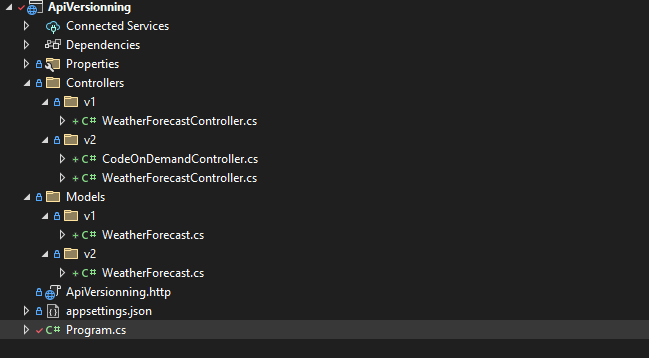
Controller
using ApiVersionning.Models.v1;
using Asp.Versioning;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace ApiVersionning.Controllers.v1
{
[Route("v{version:apiVersion}/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
[ApiVersion("1.0")]
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
{
private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[]
{
"Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool", "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching"
};
private readonly ILogger<WeatherForecastController> _logger;
public WeatherForecastController(ILogger<WeatherForecastController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
[HttpGet(Name = "GetWeatherForecast")]
public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get()
{
return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast
{
Date = DateOnly.FromDateTime(DateTime.Now.AddDays(index)),
TemperatureC = Random.Shared.Next(-20, 55),
Summary = Summaries[Random.Shared.Next(Summaries.Length)]
})
.ToArray();
}
}
}